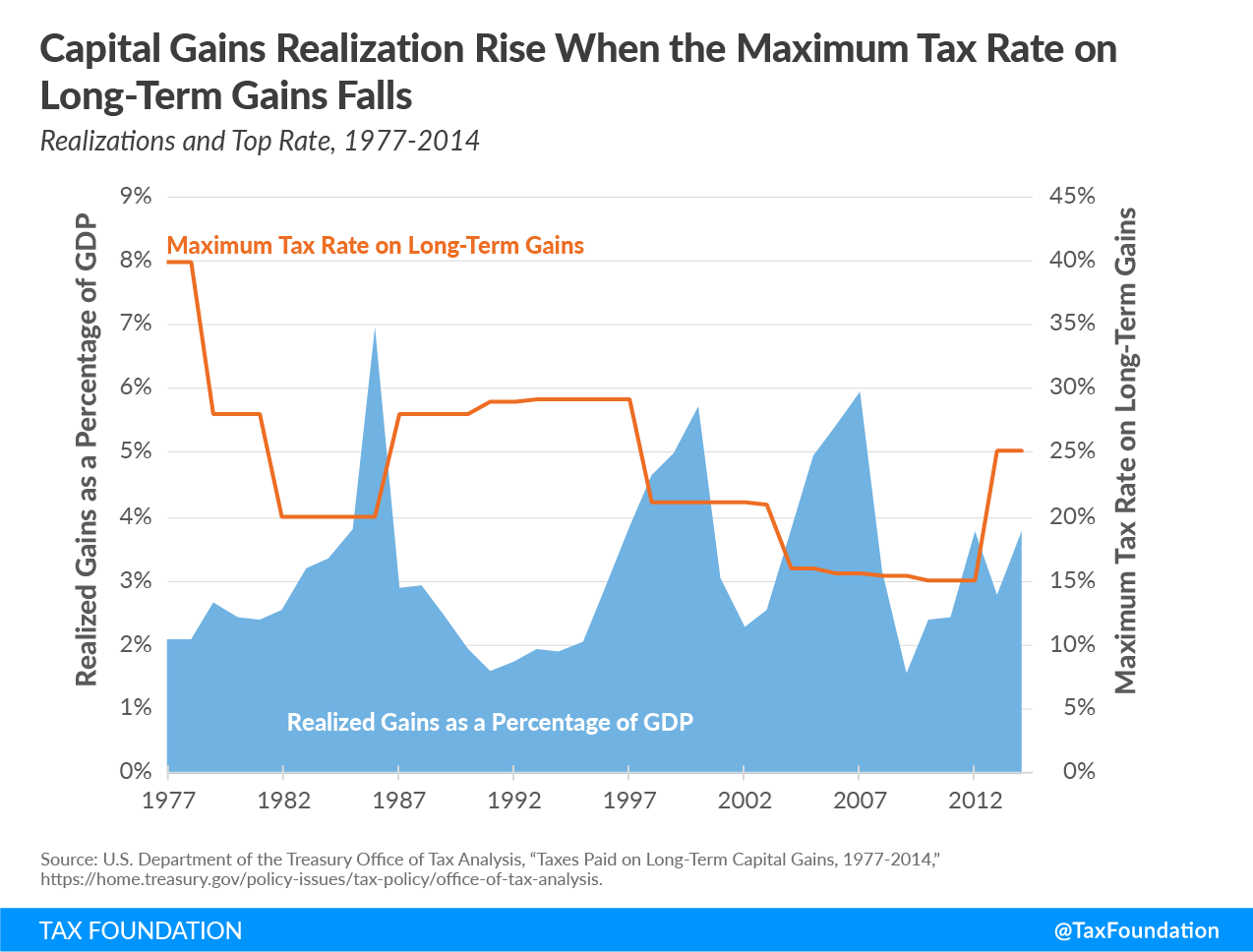
Alright folks, buckle up because we’re diving deep into the world of capital gains tax. If you’ve ever wondered what happens when you sell an asset and make a profit, this is the article for you. Capital gains tax is one of those financial terms that can seem intimidating, but trust me, it’s not as scary as it sounds. In fact, understanding it could save you a ton of money in the long run. So, let’s get started and break it down in simple terms!
Now, you might be thinking, “Why should I care about capital gains tax?” Well, here’s the deal: if you own any kind of asset—be it stocks, real estate, or even cryptocurrency—you’re going to want to know how this tax works. It’s basically the government’s way of saying, “Hey, you made some money off that sale, so we’d like a piece of the pie.” And honestly, who doesn’t love pie, right?
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let me just say this: capital gains tax is something everyone should understand, whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from the basics to some advanced tips that could help you save big time. Ready? Let’s go!
Read also:Aminah Nieves The Rising Star Whos Turning Heads
What Exactly Is Capital Gains Tax?
First things first, let’s define what we’re talking about. Capital gains tax is essentially the tax you pay on the profit you make when you sell an asset. It could be a house, stocks, bonds, or even something as trendy as Bitcoin. The key here is that you’re only taxed on the gain, not the entire amount of money you received from the sale.
For example, if you bought a stock for $1,000 and sold it for $2,000, your capital gain would be $1,000. That’s the part the IRS (or your local tax authority) is interested in. And yes, they’re gonna want a cut of that sweet profit.
Now, here’s where it gets interesting. There are two types of capital gains: short-term and long-term. Short-term gains are for assets you’ve held for less than a year, and they’re taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Long-term gains, on the other hand, are for assets you’ve held for more than a year, and they usually come with a lower tax rate. We’ll talk more about that later.
Why Should You Care About Capital Gains Tax?
Let’s face it, taxes aren’t exactly the most exciting topic, but when it comes to capital gains, there’s a lot at stake. If you’re someone who invests in assets, whether for fun or profit, understanding how capital gains tax works can literally save you thousands of dollars.
For instance, did you know that timing your asset sales could help you avoid paying higher taxes? Or that certain deductions and exemptions could reduce your tax bill? These are all things you need to know if you want to keep more of your hard-earned money in your pocket.
Plus, with the rise of online investing platforms and the popularity of cryptocurrencies, more and more people are finding themselves subject to capital gains tax. So, whether you’re flipping houses or trading stocks, it pays to be informed.
Read also:Why Vegamovies Original Is A Mustvisit For Movie Lovers
How Does Capital Gains Tax Work?
Alright, now let’s break it down step by step. When you sell an asset, the first thing you need to do is calculate your capital gain or loss. Here’s a quick formula to help you out:
- Selling Price - Original Purchase Price = Capital Gain (or Loss)
Once you’ve figured out your gain, the next step is to determine whether it’s short-term or long-term. As I mentioned earlier, short-term gains are taxed at your regular income tax rate, while long-term gains are taxed at a lower rate, which could be 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on your income level.
Now, here’s the kicker: if you have any capital losses (meaning you sold an asset for less than you paid for it), you can use those losses to offset your gains. In some cases, you can even deduct up to $3,000 in capital losses against your ordinary income. Pretty cool, huh?
Who Pays Capital Gains Tax?
So, who exactly is subject to capital gains tax? Well, pretty much anyone who sells an asset for a profit. This includes:
- Stock investors
- Real estate investors
- Cryptocurrency traders
- Art collectors
- And pretty much anyone else who sells an asset for more than they paid for it
Now, there are a few exceptions. For example, if you sell your primary residence and make a profit, you might be able to exclude up to $250,000 of that gain from taxation (or $500,000 if you’re married filing jointly). But don’t worry, we’ll cover that in more detail later.
How Much Is Capital Gains Tax?
This is probably the question you’ve been waiting for. So, how much do you actually have to pay in capital gains tax? Well, it depends on a few factors, including your income level and the type of asset you sold.
For long-term capital gains, most people will pay either 0%, 15%, or 20%. Here’s a rough breakdown:
- If your income is below a certain threshold, you might not have to pay any capital gains tax at all.
- For most middle-income taxpayers, the rate is 15%.
- Higher-income taxpayers could face a 20% rate, plus an additional 3.8% net investment income tax if they’re subject to it.
Short-term capital gains, on the other hand, are taxed at your regular income tax rate, which could be much higher. That’s why it’s often better to hold onto your assets for more than a year before selling them.
Common Misconceptions About Capital Gains Tax
There are a lot of myths and misconceptions floating around about capital gains tax, so let’s clear a few of them up:
- Myth #1: You only pay capital gains tax if you sell an asset for a profit. Truth: If you sell an asset for a loss, you might still be able to use that loss to offset other gains or income.
- Myth #2: All capital gains are taxed at the same rate. Truth: Short-term and long-term gains are taxed differently, and the rate you pay depends on your income level.
- Myth #3: You can avoid capital gains tax by not reporting your sales. Truth: Don’t even think about it. The IRS has ways of tracking these things, and the penalties for not reporting can be steep.
Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
Now that you know how capital gains tax works, let’s talk about how to minimize it. Here are a few strategies that could save you big time:
- Holding Period: Hold onto your assets for more than a year to qualify for the lower long-term capital gains tax rate.
- Timing Your Sales: Consider selling assets at the end of the year when you have a better idea of your overall tax situation.
- Using Losses to Offset Gains: If you have any capital losses, use them to offset your gains and reduce your tax bill.
- Tax-Loss Harvesting: This is a strategy where you sell losing investments to offset gains, and then immediately buy back similar investments to maintain your portfolio.
Of course, everyone’s situation is different, so it’s always a good idea to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor before making any big decisions.
Real Estate and Capital Gains Tax
Real estate is one of the most common types of assets subject to capital gains tax, so let’s talk about how it works. If you sell a property for more than you paid for it, you’ll likely have to pay capital gains tax on the profit.
However, there are a few exceptions and exclusions to be aware of:
- Primary Residence Exclusion: If you sell your primary residence and make a profit, you might be able to exclude up to $250,000 of that gain from taxation (or $500,000 if you’re married filing jointly).
- 1031 Exchange: If you’re selling investment property, you might be able to defer paying capital gains tax by reinvesting the proceeds into a similar property using a 1031 exchange.
Again, these rules can get pretty complicated, so it’s always a good idea to consult with a professional if you’re dealing with real estate transactions.
Cryptocurrency and Capital Gains Tax
With the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, more and more people are finding themselves subject to capital gains tax. Here’s how it works:
Whenever you sell or trade cryptocurrency, you’re potentially subject to capital gains tax. The same rules apply as with other assets: short-term gains are taxed at your regular income tax rate, while long-term gains are taxed at a lower rate.
One thing to keep in mind is that the IRS considers cryptocurrency to be property, not currency. That means every time you use crypto to buy something, it’s considered a taxable event. So, if you bought a coffee with Bitcoin, you might owe capital gains tax on the difference between what you paid for the Bitcoin and its value at the time of the purchase.
Tax Planning Tips for Investors
Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, there are a few things you can do to make tax season a little less painful:
- Keep Good Records: Make sure you keep track of all your purchases, sales, and any associated fees or expenses. This will make it easier to calculate your capital gains and losses when tax time rolls around.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re dealing with complex investments or large transactions, it’s always a good idea to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor.
- Stay Informed: Tax laws can change, so make sure you stay up-to-date on any new regulations that could affect your investments.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Capital Gains Tax Matters
Alright, we’ve covered a lot of ground here, so let’s wrap it up. Capital gains tax might seem complicated at first, but once you understand the basics, it’s really not that bad. Whether you’re flipping houses, trading stocks, or dabbling in crypto, knowing how this tax works can help you keep more of your money in your pocket.
Remember, the key is to plan ahead and make smart decisions. Hold onto your assets for the long term, use losses to offset gains, and don’t be afraid to seek professional advice when you need it. And most importantly, always keep good records!
So, what do you think? Are you ready to take control of your capital gains tax situation? Leave a comment below and let me know what you think. And if you found this article helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends and family. Who knows, you might just save someone a bundle of cash!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is Capital Gains Tax?
- Why Should You Care About Capital Gains Tax?
- How Does Capital Gains Tax Work?
- Who Pays Capital Gains Tax?
- How Much Is Capital Gains Tax?
- Common Misconceptions About Capital Gains Tax
- Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
- Real Estate and Capital Gains Tax
- Cryptocurrency and Capital Gains Tax
- Tax Planning Tips for Investors